Appearance
AireFlow Commands
A library of test commands to use when testing AireFlow
Identifying the AireFlow Flow to Test
AireAssert will need to know which recorded flow in AireFlow to inspect. Our AireSuite products are joined together with a CorrelationId - created by the first product interacted with by a user (usually a form) and passed through to all subsequest products. If you have submitted a form as part of your test then you don't need to do anything - subsequent assertions will target flows triggered by your form.
If you do not have a form to trigger with, but you know the CorrelationId of your flow you can set this up with a GIVEN step:
gherkin
Given a Correlation ID of 'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'Triggering a Flow
For information on how to setup a trigger on AireFlow, please see the AireFlow Documentation site
While ideally you will trigger a flow with a form submission, it is also possible to directly trigger a flow. You will need the routing key of the event that triggers the flow. You can find this under Event Definitions in your target AireFlow instance.
Next you will need a payload to send, this is a block of XML. Add an XML file within an 'AireFlowPayloads' directory in your Test Set:

Your payloads can be templateable. In your XML use the --TOKENNAME-- format to show where data can be passed in, e.g.
xml
<myparent>
<mynode>--*some-token*--</mynode>
</myparent>Now we are ready to trigger the flow:
gherkin
When we trigger aireflow event 'xxx' with payload 'xxx'
| some-token | Value to inject into XML |
| some-other-token | Some other value |The command succeeds if AireFlow accepts the trigger.
AireFlow Tasks
An AireFlow task represents a single action within a workflow. You refer to a task using its key, and can then assert on its State or Properties
To find the key for your task, view it in the AireFlow designer:
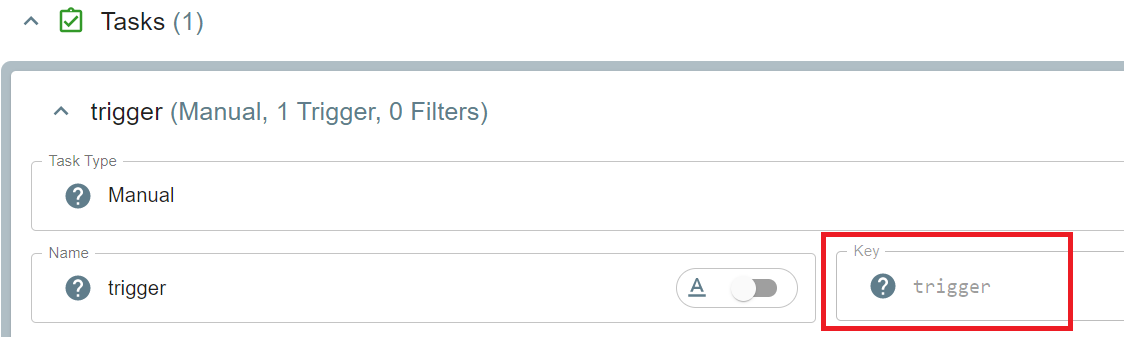
Asserting a Task Has Run
We can confirm that a task has been run:
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has been run
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has been run within x secondsChecking Task Status
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has status of 'xxx'
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has status of 'xxx' within x secondsState Assertions
Each task can have state assigned, this is a set of key/value pairs which you can see in the API definition
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has state
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has state within x secondsVerifies that the specified task has some state assigned, either now or within the timeout period specified.
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xx' has state 'xxx' of 'xxx'
Then aireflow task 'xx' has state 'xxx' of 'xxx' within x secondsVerifies that the specified state value exists on a task, either now or within the timeout period specified.
Property Assertions
A property is any of the basic properties available under ActivityContext in the API Definition
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xx' has properties
Then aireflow task 'xx' has properties within x secondsVerifies that the task has properties, either now or within the timeout period specified.
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xx' has property 'xx' of 'xx'
Then aireflow task 'xx' has property 'xx' of 'xx' within x secondsVerifies that the specified Property value exists on a task, either now or within the timeout period specified.
Verifying Task Metadata
- Name
Assert the task’s display name with a “has name ‘TaskName’” step (optionally within a timeout).
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has name 'xxx'
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has name 'xxx' within x seconds- Description
Assert the task’s description text with a “has description ‘TaskDescription’” step (optionally within a timeout).
gherkin
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has description 'xxx'
Then aireflow task 'xxx' has description 'xxx' within x seconds